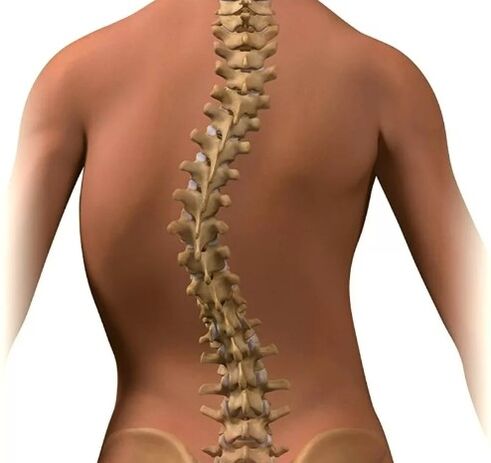
In Greek there is the word “scolios”, which translates as “crooked”.With this word, doctors denote the curvature of the spinal column.Moreover, not all curvature, namely the lateral deviation of the vertical axis of the spine.The fact is that normally our spine is not perfectly even.The bends available in the front and back (lordoses and kyphosis) protect our spine from excessive loads while maintaining the body in a certain position when moving and carrying weights.Negative processes in our body develop only in cases where these kyphoses and lordoses are expressed in excess of the permissible norm.
The main problems
However, even a small degree of lateral bends (scoliosis) of the spine is always a pathology.And the point is not only in a cosmetic defect.Although a characteristic repulsive appearance with pronounced or progressive scoliosis is always a tragedy for a person who seeks to live a high -quality full life.This is especially true for young boys and girls.Indeed, it is in the children's and youth period (up to 15 - 16 years) that a significant part of scoliosis is diagnosed.
The main problem is that due to a change in the configuration and volume of the chest with pronounced lateral curvature, internal organs always suffer (heart, lungs, stomach, liver, intestines, large vessels).In men, tolerance to physical exertion decreases, women have problems with conception, bearing pregnancy and childbearing.Moreover, very often the lateral deformation of the spine is just the surface part of the iceberg, which is a sign of a much more serious pathology - tumor, tuberculosis, endocrine disorders.
Reasons
So why is the spine deformed?Before answering the question, you should decide on the types of scoliosis.At its core, scoliosis can be structural and unstructural.Structural scoliosis develop due to anatomical changes in the structure of the bone tissue of the vertebrae, as well as the muscles, nerves, and ligamentous apparatus located nearby.Such curvatures can be acquired and congenital, and about a quarter of all diagnosed scoliosis accounts for the latter.
Among the main reasons for the development of structural scoliosis, they distinguish:
- Masts of intrauterine development leading to dysplastic disorders of one or more vertebrae
- Congenital chest development abnormalities - lack of ribs, additional ribs
- Congenital pathology of connective tissue - neurofibromatosis, marfan syndrome
- Brain failure due to children's cerebral paralysis (cerebral palsy), leading to a violation of innervation of certain parts of the spine
- Osteoporosis (bone -tissue) of the spine in rickets, diseases of the parathyroid glands, a lack of calcium intake with food
- Osteomyelitis of the vertebrae
- Dystrophic changes in cervical, thoracic and lumbar muscles
- Tuberculosis damage to the vertebrae
- Spinal injuries
- Tumors of the spine.
Non -structural scoliosis, as follows from the very name, is the lateral deviations of the axis of the spinal column with the unchanged structure of the vertebrae.As a rule, such scoliosis is most often acquired with the exception of cases where curvature is compensatory in nature with congenital anatomical defects of the pelvis or lower extremities.The causes of such scoliosis are most often:
- Pelvic injuries and lower extremities
- Congenital defects of the pelvis and lower extremities
- Constant improper posture in schoolchildren
- Diseases of internal organs with asymmetrically expressed pain syndrome
- Muscle inflammation (myosites)
- Burns, scars of soft fabrics on one side.
In these cases, to eliminate the curvature of the spine, it is enough to cure the underlying disease, and therefore many unstructural scoliosis are easily reversible.In this regard, some doctors tend to not reckon unstructural deformations for scoliosis in general.
Recently, cases of development of scoliosis with unclear causes have become more frequent.This is the so -called idiopathic scoliosis.It occurs in the youth years, during the period of rapid growth of the body.Moreover, girls suffer from idiopathic scoliosis several times more often than young men.Apparently, this is due to the relatively weak muscles of the back of the female, which is not able to enclose the spine in a full muscle frame.An unbalanced diet with low calcium salts, and a general passion for youth with carbonated drinks plays a not the last role in the development of idiopathic scoliosis.As you know, carbon dioxide in bubbles and orthophosphoric acid in synthetic inclusions contribute to leaching of calcium salts from the body.
Varieties and degrees
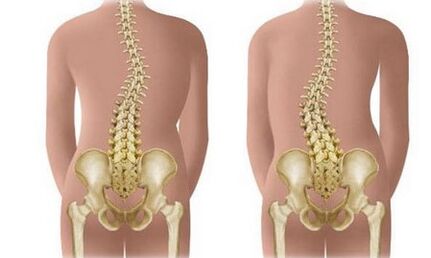
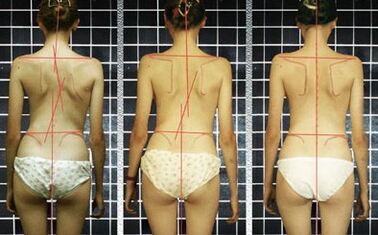
Depending on the localization, scoliosis can be cervical, chest, lumbar or mixed (cervical, lumbosacral).It is possible to have one or more curvature arcs.In this regard, C-shaped scoliosis (with 1 arc), S-shaped (with 2 arcs) and Z-shaped (with 3 arcs) are distinguished.Most likely, the presence of 2 or 3 arcs is compensatory.With C-shaped scoliosis, the axis of the spinal column deviates.In an effort to compensate for this, the spine bends in the opposite direction.In this regard, scoliosis is divided into compensated and uncompensated.In compensated spinal curvature, a vertical line lowered from the 7th cervical vertebra passes through the fold between the buttocks.
The curvature of the spine is often combined.For example, in the thoracic region, in addition to lateral curvature, pathological kyphosis is noted, or simply a hump.In these cases, speaking of thoracic kyphoscoliosis.In addition, with large degrees of scoliosis, in addition to the lateral displacement of the vertebrae, Thuria is noted.In a literal translation, this means twisting.Indeed, with many scoliosis, the vertebral bone tissue is twisted along the vertical axis.
Depending on the size of the angle of the arc of curvature, 4 degrees of scoliosis are distinguished:
- 1 degree- The angle of curvature does not exceed 10 degrees.Asymmetry by eye is practically not determined.The stoop, the unequal level of the shoulder girdle, pays attention.
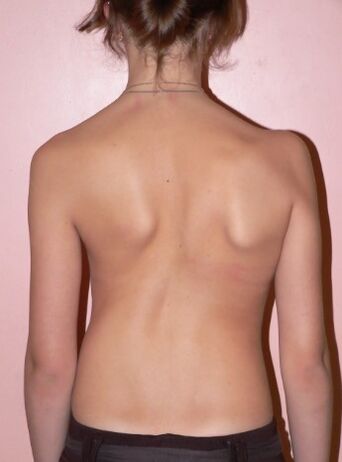
- 2 degree- The angle of curvature is from 11 to 25 degrees.In this extent, the vertebrae is already noted.There is an asymmetry of the shoulder girdle and pelvis that is visible on the eye.Due to the pathological muscle tension, a muscle roller is formed in the lumbar region from the concave side, and in the chest area-with a convex.
- 3 degree- Wrtification is from 26 to 50 degrees.Visible deformation of the chest - the western of intercostal spaces C in the concave side of curvature and bulging with convex.Weakening of the abdominal press, the formation of an internal hump.
- 4 degree- The angle of curvature I exceeds 50 degrees.A cosmetic defect and all previous signs are expressed.Low tolerability of even small physical exertion.In addition to the musculoskeletal system, internal organs suffer.
The angle may vary depending on the position of the body, while stable and unstable scoliosis is distinguished.With unstable scoliosis, it decreases in the lying position when the load on the spinal column decreases.With a stable curvature of the spine, this value remains unchanged.
Symptoms
Recently, orthopedists often use the term “scoliotic disease”.And they indicate a complex of negative changes that occur in the body during curvature of the spine.As a rule, scoliotic disease develops in childhood and adolescence, during the formation of the musculoskeletal system.At this time, there is a high probability that scoliosis will progress.
Apparently, intervertebral discs play an important role in increasing the angle of curvature.With a side displacement, the disk experiences unequal pressure from the vertebral bodies.On the concave side, this pressure is greater, with a convex - less.As a result of this, the disk wears out even more from scoliosis, a pathological muscle tension (muscle roller) and torsion of the vertebrae is created - all this leads to the appearance of disk hernias and to a further increase in the angle of curvature.
Along with the spine with a scoliotic disease, the chest changes secondly.The so -called rib hump is formed - on the convex side of curvature, the intercostal spaces expand, and from the concave - on the contrary, they are sown.With scoliosis of the 4th degree, the deformation of the chest is so pronounced that the lower ribs on the side of the curvature are in contact with the rowing of the iliac bone.
Due to severe deformation of the chest, a full-fledged excursion during breathing is difficult.As a result, the body with severe scoliosis does not receive the required amount of oxygen - the so -called chronic hypoxia develops with a violation of all metabolic processes in the body.The pathology is aggravated by the fact that the internal volume and shape of the chest cavity change.Because of this, blood circulation through the vessels is disturbed, the lungs suffer, the shape of the heart changes, chronic cardiovascular failure develops.
Similar changes occur in the abdominal organs for the lumbar and lumbosacral scoliosis.Motorics of the stomach and intestines are reduced with subsequent enzymatic insufficiency of the digestive glands.All this only exacerbates metabolic disorders.These violations often lead to belated sexual maturation of boys and girls.In addition, due to lumbar scoliosis, the pelvis is curved a second time.This creates problems for future mothers with gestation and childbearing.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of scoliosis, especially large degrees, as a rule, is not difficult.To detect deformation of the spine, a common visual examination is often enough.The visible curvature of the contours of the spine, the asymmetry of the shoulder girdle, the angles of the shoulder blades, the secondary curvature of the pelvis and the shortening of the lower limb on the side of the curvature are noteworthy.
In the presence of at least one of these signs, radiography of the spinal column is indicated.The X -ray determines the configuration, degree and localization of curvature.During the inspection and radiological examination, it is possible to establish whether scoliosis is compensated and stable.Recently, a qualitatively new method of research of the spine-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been spread, during which a three-dimensional image of the spine can be obtained on the monitor screen.With significant curvatures, it is necessary to investigate the work of internal organs - to carry out a spirometry, electrocardiography, and carry out an ultrasound of the heart and internal organs.
Treatment
Treatment of scoliosis can be carried out both conservatively and promptly.Conservative methods include drug treatment, massage, physiotherapeutic procedures, and manual therapy.It should be borne in mind that the final formation of the spine ends by the age of 20, and after this age, the correction of curvature is almost impossible.With scoliosis of 1-2 degrees, efforts are aimed at achieving the initial, normal configuration of the spine.With pronounced scoliosis of the 3rd - 4th degree, this is unattainable, the main thing here is to stabilize the spine and prevent the progression of scoliosis.
Medicines (chondroprotectors, vitamins, general strengthening drugs) in the treatment of scoliosis play only an auxiliary role.To strengthen the muscles, eliminate the muscle roller, and even to a large extent to stabilize the spine with the help of massage and manual therapy.A good effect is given by physiotherapy exercises.But here, with inadequate physical exertion, the instability of the spine is enhanced and scoliosis progresses.Therefore, a set of exercises is developed for each patient individually, taking into account the localization and severity of curvature.With a large degree of scoliosis, running, strength exercises, jumps, outdoor games are contraindicated.
A very good result gives correction by the position - the optimal pose is created that contributes to the normalization of posture.For this, special devices are used, orthopedic cribs in which young patients spend a significant part of their time.With the ineffectiveness of conservative measures, the progression of curvature, surgical treatment aimed at stabilizing the spine is indicated.Surgical correction is not shown in early childhood, it is carried out in adolescence, when the formation of the spine is almost completed.

















































