Cervical osteochondrosis — a degenerative-dystrophic process in the intervertebral discs of the cervical spine, accompanied by the replacement of cartilage by bone tissue and immobilization of the vertebrae. According to statistics, certain degenerative changes in the cervical spine are present in about half of persons of working age – from 25 to 45 years.
Causes and risk factors
Anatomical features of the cervical spine create the prerequisites for early development of degenerative changes. The vertebrae of the cervical segment have maximum mobility, perform all kinds of movements fully and therefore prone to early wear.
On the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis you should think in childhood.
To the development of cervical degenerative disc disease has a sedentary lifestyle, especially the habit of sitting, craning her neck forward, which increases pressure on the intervertebral discs, leading to deformation and dewatering pulpous nucleus. Degeneration of cartilage aggravate the trophicity because of compression of blood vessels spazmirovannah muscles. Progressive for cervical degenerative disc disease caused by the following factors:
- congenital malformations of the structure of the vertebrae;
- endocrine disorders;
- autoimmune collagen diseases (rheumatic fever and systemic lupus erythematosus);
- torticollis in newborns;
- dysplasia head of the hip joint;
- flat feet;
- posture and curvature of the spine;
- trauma and microtrauma to the cervical vertebrae;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse;
- prolonged emotional distress;
- genetic predisposition.
The development of cervical degenerative disc disease also contributes to long-term intoxication when staying in ecologically unfavorable areas, regular contact with harmful substances and the presence of chronic foci of infection in the body.
Symptoms of cervical degenerative disc disease
In the early stages of degenerative-dystrophic process, the disease is almost asymptomatic. Discomfort in the neck occur only at sudden movements after prolonged sedentary posture tense and inclined head position or in response to excessive exercise. The development of myositis accompanied by a feeling of stiffness, and a clear location of pain points to spasms in the neck muscles.

Decompensated cervical osteochondrosis is characterized by a persistent discomfort in the neck, habitual tension of the muscles and limitation of motion of the cervical segment; the forced position of the head partly smooths out the discomfort. When turning or tilting the head frequently hear the crunch of the vertebrae. Subluxation of the intervertebral joints accompanied by sharp burning pain, which is popularly called the cross, and vegetative disorders: aching headache, dizziness, blackouts, palpitations, etc. a Spontaneous reduction of the subluxation brings quick relief.
In the case of formation of osteophytes and extrusions on the rear surface of the vertebrae common manifestations of cervical degenerative disc disease later added radicular symptoms:
- headaches localized in the occipital and parietal region;
- the reduction of skin sensitivity on one side of the neck;
- disturbance of speech and numbness of the tongue;
- discomfort in the outer surface of the shoulder;
- respiratory disorders.
With the defeat of osteochondrosis of the third cervical vertebra is sometimes observed reflex kardialgichesky syndrome – a severe pain behind the breastbone radiating to the scapula and shoulder, causing Association with a heart attack, especially if the soreness is accompanied by heart palpitations. In the case of destruction of the three lower vertebrae pain and paresthesia extend from the neck to the shoulder, forearm, hand and fingers. Patients may complain of numbness of the upper extremities, burning sensation, tingling or "pins and needles" along the nerves.
To the development of cervical degenerative disc disease has a sedentary lifestyle, especially the habit of sitting, craning her neck forward.
Osteophytes located on the lateral surfaces of the vertebrae compress the vertebral artery, causing a range of disorders of cerebral circulation, which is called the vertebral artery syndrome. This pathology is manifested by frequent attacks of pressing headache, which extends from the nape to the crown and temples, giving to the eyeballs. In some cases, headache is the steady feeling of heaviness in the head. Simultaneously observed in autonomic symptoms:
- changes in blood pressure;
- bouts of palpitations and arrhythmias;
- migrenepodobna unilateral pulsing headaches, accompanied by photophobia, nausea and vomiting;
- disorders of thermoregulation (chills, sweating, cold extremities);
- dizzy spells, fainting and drop attacks.
- violation of coordination of movements;
- noise and congestion in the ears;
- the decrease in visual acuity and visual disorders: darkening and diplopia, blurred vision, flashes and colored flies before the eyes;
- sleep disorders;
- fatigue and emotional lability.
Diagnosis
Because of low specificity of symptoms and a great diversity of manifestations diagnosis of osteochondrosis is conducted in several stages. We should start with a consultation with a specialist – surgeon, orthopedist, neurologist or vertebrologist. Presumptive diagnosis becomes based on the patient's complaints, anamnesis and data of physical examination. During examination of the patient, the doctor draws attention to the mobility of the neck, the sensitivity of the skin and painful areas in the cervical segment and the shoulder girdle, strength and muscle tone, the severity of tendon reflexes.
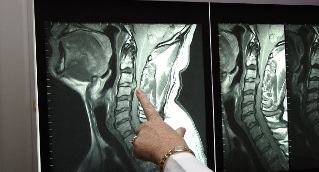
To determine the stage of the pathological process and identify complications of the patient is directed to MRI of the cervical spine. Thanks to high-quality visualization of hard and soft tissue on tomograms are all signs of cervical degenerative disc disease – reduction of height of intervertebral disks, osteophytes, protrusion, extrusion, damage to nerves and blood vessels, calcification of ligaments, pockets of bone tissue, myositis and congestion in the muscles.
Doing household chores you can't stand on tiptoe or to keep their hands raised over the head; it is better to use a stepladder or stand on a stool.
In case of unavailability of MRI conducted x-rays or CT of the cervical segment to identify osteophytes, osteoarthritis and reduced bone density. Changes of the soft tissues visualized by ultrasonography; to study the hemodynamics and the assessment of the degree of damage to blood vessels in case of advanced cervical osteochondrosis appoint dopplerography of neck vessels, and in cases of suspected infringement of the spinal cord – contrast myelography.
Treatment of cervical degenerative disc disease
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine requires a comprehensive treatment. During exacerbations the primary goal of therapy is to relieve pain, the relief of the inflammatory process and restoring the capillary circulation to affected areas. Patients are prescribed analgesics or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, of which the preferred inhibitors of cyclooxygenase-1 on the basis of diclofenac and nimesulide. In severe muscle spasms are advised to wear an orthopedic collar; if necessary, prescribe antispasmodics and muscle relaxants.
When radicular syndrome with poor response to medical treatment have resorted to x-ray-controlled blockades infringed roots and steroid injections. To improve metabolism in the intervertebral discs and damaged nervous structures shown a course of vitamins of group B. Complicated extrusion and pinching of the spinal cord, and intractable pain syndrome are indications for surgical intervention.
Full restoration of intervertebral disks in osteochondrosis is unlikely, but with the help of timely and adequate therapeutic measures can stop or slow the progression of degenerative process.
As the attenuation of the acute symptoms begin a course of physical therapy aimed at activation of the blood supply in damaged areas and disposal of the products of inflammation. Well established electrophoresis and phonophoresis, magnetotherapy, amplipulse therapy, Shockwave therapy, UHF and diadynamic.
Rapid restoration of mobility of the cervical contribute to the classes in group exercise, swimming and Aqua fit. To learn at home: the most effective exercises with cervical osteochondrosis require no special equipment and exercise machines. The daily program of rehabilitation takes 15-20 minutes and consists of five simple exercises. Each exercise is repeated 5 times in a slow smooth pace, gradually increasing the number of repetitions to 10-12 times.
- The turning and rotating the head right and left in a fixed position head and shoulders.
- Alternate pressing his forehead and the back of his head on the palm with a slight tension in your neck.
- The tilt of the head, thrown back, to the jugular fossa and to the side. When tilted to the right need to touch right ear to right shoulder and left ear to left shoulder.
- Pressing the left temple on his left hand, then right temple at the right hand.
- The tilt of the chin to the neck with the head turning first right, then left.
To the means of alternative medicine should be treated with great care and to coordinate their use with your doctor. In the absence of contraindications, you can take a course of acupuncture, hirudotherapy and osteopathy; manual therapy is strictly contraindicated. Ordinary therapeutic massage with cervical osteochondrosis gives more promising results without exposing the patient to unnecessary risk.
Possible complications and consequences
In the neck there is a large amount of the autonomic nerve plexus and blood vessels, including the vertebral artery and spinal nerve. The joints that connect the speakers front edges of the vertebrae are prone to dislocations and subluxations, and the triangular shape of the intervertebral foramen in the lower three cervical vertebrae increases the likelihood of infringement of the nerve roots by bone spasserovannye glands and muscles. As a result, the risk of secondary compression syndromes in cervical osteochondrosis higher than in lesions of other parts of the spine.
In the early stages of the disease complications are mainly associated with myositis and muscle spasms. The syndrome of anterior scalene muscle develops with prolonged compression of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery spazmirovannah anterior scalene muscle. Reflex stimulation of autonomic nerve fibers and insufficient blood supply to muscle tissue is manifested by soreness of the forearm and wrist that increases with downward position of the head and the movement of an arm. If by displacement of the large vessels marked swelling and cold limbs.
The appearance of extrusions and osteophytes accompanied by radicular syndromes which, in turn, may be complicated by entrapment of the spinal cord. Compression of the spinal cord often causes paralysis of the upper extremities, and in severe cases leads to death due to the acute oppression of respiratory function. Severe vertebral artery syndrome accompanied by severe ataxia and decompensated neurocirculatory dysfunction threatens to turn into a disability and increases the risk of ischemic stroke and of spinal cord ischemia.
Forecast
Full restoration of intervertebral disks in osteochondrosis is unlikely, but with the help of timely and adequate therapeutic measures can stop or slow the progression of the degenerative process, prevent complications and achieve maximum preservation of mobility of the cervical. In case of advanced degenerative disc disease of the cervical spine, complicated by multiple extrusions, and compression syndromes, the prognosis is more careful.
Prevention
On the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis you should think in childhood. The formation of correct posture, consistent strengthening of the muscle corset back and nutrition will help to maintain the health of the spine in adulthood. In identifying the child's incorrect posture, flatfoot and effects of birth injuries such as torticollis and dysplasia of the head of the hip joint, should not be neglected rehabilitation programs: a pathology of locomotor apparatus associated with degenerative disc disease, are successfully treated before the ossification of the skeleton.

If the profession of the patient assumes a sedentary lifestyle, you need to find an ergonomic office chair with neck support, and a set of bedding to include pillow top mattress and low firm pillow. To sleep on soft couches and beds with tubular mesh is not recommended; it is better to choose a model with a moderately hard smooth surface. During operation, every 45-60 minutes, it is desirable to perform the exercises for the neck, and to relax, to exercise and more likely to walk. Good effect is given swimming lessons and water aerobics, yoga, qigong and Pilates classes; power and traumatic sports is better to exclude. During class, avoid sudden movements and keep your back straight. Doing household chores you can't stand on tiptoe or to keep their hands raised over the head; it is better to use a stepladder or stand on a stool. Two or three times a year will not hurt to undergo treatment-and-prophylactic massage of cervical-collar zone.
The diet should be adequate protein, vitamins and minerals should be included in the menu of the jelly, jellied fish and seafood are natural sources of collagen. Avoiding harmful habits contributes to the maintenance of active circulation in the intervertebral discs.

















































