Osteochondrosis — degenerative changes affecting the intervertebral discs, joints, ligaments and other tissues that form the vertebral-motor segment (PDS). This disease primarily affects the intervertebral discs and secondarily other parts of the spine and musculoskeletal system. It is considered that the greatest prevalence of this disease occurs in relatively young people and people of middle age, with a tendency to decrease in elderly and senile age.
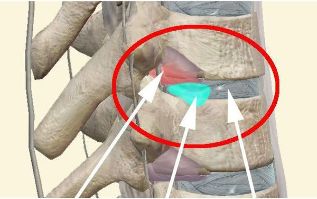
The composition of the spinal motion segment includes two adjacent vertebrae, the upper and niinamesai. Between them is intervertebral disc, articular joints and spinous processes. Neighboring vertebrae between the articular processes form an articular connection (bootnote, or facet joints). The spinous and transverse processes of the vertebrae are held together by the surrounding ligaments. This design along with the discs and provides spine mobility and stability.
The causes of osteochondrosis are still not defined. However, the fact that it is common in certain professional categories of adults, suggests that the leading cause of this disease is sedentary lifestyle. As a result of lack of muscle loads reduce physical muscular effort and replacing them with static body parts that by nature needs to be movable (neck, waist) is a weakening of a spring and stabilizing functions of muscles.
Degenerative changes of the spine occur as a result of:
- excessive static or dynamic loads on the spine (e.g. lifting weights);
- hereditary predisposition;
- confirmed spinal cord injuries in the past.
At detection of similar symptoms consult a doctor. Do not self-medicate is dangerous for your health!
Symptoms of degenerative disc disease
The primary symptom of low back pain — myofascial pain syndrome, it is a painful spasm of the muscles, which is a consequence of muscle dysfunction.
Speaking about the reasons for the occurrence of pain, release pain that is caused by an abnormality of the structures of the spine (or vertebral pain syndromes), or pain of other origin (nevertebralnah pain). What kind of pain is revealed, depends on the choice of methods of treatment.
The types of back pain:
1. Nociceptive — due to the fact that peripheral pain receptors affected by various precipitating factors (trauma or inflammation) if intactness all parts of the nervous system. For such pain characterized by the appearance of zones of constant pain and increase pain sensitivity in areas of tissue damage.
2. Neuropathic — arising as a result of pathological stimulation of neurons in the peripheral or Central nervous system responsible for response to physical damage to the body. Often, a characteristic symptom of neuropathic pain is the reduction of muscle strength and sensitivity, manifested, in particular, the fact that the patient feels pain in response to stimuli nabolese.
3. Dysfunctional (psychogenic) — occurs as a result of changes in the functional state of the nervous system or altered human perception. Often there is an increased rest after strenuous activity.
4. Combined — is a combination of several varieties of pain, as described earlier.
Usually back pain is associated with irritation of pain receptors of muscles, joints and ligaments, and the pain is nociceptive in nature. The patient feels it in the place of origin (local pain) or distance (referred pain). Neuropathic pain is usually associated with the fact that the process involved Karasek nerve or the spinal ganglion. Such pain is chronic.
Reflected back pain caused by disease of internal organs (in other words, viscerogenic pain).
Taking into account the causes of low back pain, clinical manifestations of the disease may be associated with a herniated disc or degenerative (pathological) changes in the spine (for example, arthrosis of the intervertebral joints or formation of osteophytes).
4 main clinical syndrome, which can lead to each of the above options:
- local local pain;
- reflected (reflex pain) associated with disorders of the osteo-muscular (fascial) structures;
- radicular syndromes (radiculopathy), caused by the irritation or compression of the cerebrospinal roots;
- myelopathy – pain resulting from compression of the spinal cord or its vessels.
The pathogenesis of osteochondrosis
The basis for the development of osteochondrosis is a series of pathophysiological mechanisms. The disease develops as a result of degenerative processes, which originate at an early age, as well as aseptic inflammation, dystonia, spasm.
When changes occur in the spine the intervertebral disc at the beginning there is damage to the sheath around nerve fibers (demyelination), then the observed damage processes of nerve cells (axonopathy), local decrease in circulation (ischemia) and further venous stasis. The combination of these processes exacerbates the situation, and if there is no timely treatment, it leads to peripheral or Central sensitization.
Often there is loss of the nucleus pulposus and the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc. The mechanical stresses lead to elastic fibrous ring of the disc loses its elasticity and it is bulging. Then through the cracks of the annulus occurs the loss of the plots of the nucleus pulposus of the spine, i.e. a disc protrusion is replaced by a disc herniation.
A herniated disc is called a solid education, which sohranyaet connection with the body of the intervertebral disc, but sometimes occurs the loss of the fragments in the spinal canal (sequestered disc).
Classification and stages of development of degenerative disc disease
From the localization point of view there are following types of diseases:
- lumbalgia — pain in the lumbar (lumbar-sacral) back;
- sciatica — back pain radiating to legs;
- lumbago — lumbar lumbago, i.e. sharp intense pain in the lower back;
- torakalgiya — pain in the chest;
- cervicalgia, cervicobrachialgia — pain in the neck and upper extremities.
Classification of stages of development of an osteochondrosis:
Stage 1: reduces the amount of moisture, the intervertebral disc loses its elastic properties, and loads remain the same. As a result, the disc decreases in height, flattened, there is a protrusion.
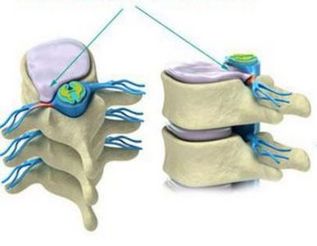
Stage 2: if the pathology continues to develop in the fibrous ring, the appearance of cracks, and as the height of the flattened disk is already reduced, then the result of this is the instability condition of the spinal segment.
Stage 3: the education gap in the cartilage tissue of the annulus. Through it seeps the more liquid part of the nucleus and the formation of a herniated disc. Such changes are often found in the lumbar and cervical spine.
For the first time the pain in the presence of a herniated disk occurs when there is irritation of the pain receptors of the outer layers of the annulus fibrosus and posterior longitudinal ligament.
Complications of degenerative disc disease
- The symptom of lumbago. In the early stages marks the onset of recurrent pain as a response to some action, for example, as the result of sudden movements, heavy lifting, heavy load (long walk), a long stay in obezbijede position. This kind of pain is familiar to many and is described as "grab". Is a rare occurrence, activating a movement, and almost does not manifest itself in a static position. This type of pain is not serious consequences, and he independently passes during the week.
- Lumbalgia. This kind of pain tends to worsen with hypothermia, having intense during the movement. Is not a reaction to the load on the spine, in a stationary state does not stop, though subsides, leaving aching feeling.
- Sciatica. The pain experienced in neighboring departments. Lumbar osteochondrosis is characterized by irrationalism pain in the leg, the chest — in the area of hand or heart; of the neck is manifested by migraines.
- Convulsions. They are often subjected to the triceps muscle of the calf. In addition, the appearance of very severe pain when touched in the back or legs.
- Coccygodynia. Irradiiruet in the coccyx, or groin. Pain-aching, burning, sterledeva nature, which can drastically limit the physical activity of the patient
Diagnosis of degenerative disc disease
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis involves several stages:
1. History collection. At this stage, examines patient complaints and history of disease. In conversation with the patient it turns out, which is mostly localized discomfort, their intensity, duration, the factors causing the increased pain and contribute to pain relief. In addition, in the diagnosis the important point is the clarification of the history of the disease: the emergence of unpleasant sensations and stiffness; identify probable causes of their occurrence; collect information about the earlier treatment and its effectiveness; collect information about the latest aggravation and the nature of its flow. For the diagnosis also is important to clarify the conditions in which the patient lives and works, what kind of life what kind of bad habits is what suffered illnesses and injuries, will be important and consideration of a genetic factor.
2. During the physiological examination evaluation of body position of the patient's gait and movements; skin (for redness, rashes, peeling), compares symmetrical areas of the body healthy and the painful side; it is determined by the range of motion (bending, circular movements of the body, the amount of rotational movements in different parts of the spine); palpable painful areas to determine skin temperature, the presence of spasms in the muscles, swelling, painful seals; palpation of the deep and superficial layers of muscle allows you to assess the condition of the muscular system (muscle tone, increase or decrease their volume); with the help of tapping with a special hammer or a finger is determined by the area of irradiation of the pain with tingling, needle pain sensitivity is determined; at the end of a number of special techniques to find out the symptoms of radicular tension.
3. The x-rays. For the best informative study is made of each spine individually. Is performed in two oblique projections in two mutually perpendicular planes (axial and lateral). In some cases, you can assign functional radiographs, when the patient is in the flexion, extension or lateral bending. Special indications for obtaining better results the study was conducted with the introduction of contrast agents into the spinal canal in the vertebral or carotid artery in the damaged intervertebral disc or spinal angiography, discography, myelography, pneumonologia.
The main radiological signs of osteochondrosis consider:
- abnormal mobility of the vertebrae;
- the displacement of their bodies;
- calcification of disc (salts);
- uniform narrowing of the intervertebral slit in the lumbar and cervical, and thoracic narrowing wedge-shaped;
- the formation of osteophytes (marginal growths);
- education on the border with the affected disk seal (marginal sclerosis).
5. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is based on the fact that the applied electromagnetic waves that create the signal characteristic for each tissue. It is processed by the computer and translated into a graphical image. Using this method it is possible to clearly see blood vessels, nerve fibres and intervertebral discs without the harmful effects of ionizing radiation on the body.
Forecast. Prevention
As practice shows, the majority of manifestations of degenerative disc disease when properly conducted therapy, the approval occurs within 6 weeks.
However, incorrectly chosen treatment or self-medication can lead to the fact that pain will become a chronic condition and will contribute to the aggravating changes in the spine in the future.
When pain in the back or limbs, you must first consult a qualified professional for proper diagnosis and appointment of adequate treatment.
The most efficient and effective method for treating most manifestations of back pain is medication and injection therapy and acupuncture. Physiotherapy, including laser therapy, massage, spinal manipulation have little bad effect, and in some cases may be completely contraindicated.
Modern methods of treatment of osteochondrosis is based on the principle of continuity of treatment: that is, rapid and safe relief of acute episode of pain followed by the inclusion of preventive methods. In order to prevent the emergence and development of degenerative disc disease can be recommended, first of all, weight loss (if overweight) and regular physical activity.
Regular sessions with the technique of dynamic muscular stabilization (yoga, Pilates within aerobic exercise) is the basis of rehabilitation and prevention of back pain, improves strength and endurance of the muscles of the spine.

















































