Knee osteoarthritis — a progressive degenerative pathology. First, it affects the cartilage and then in the destructive process involves bony structures.
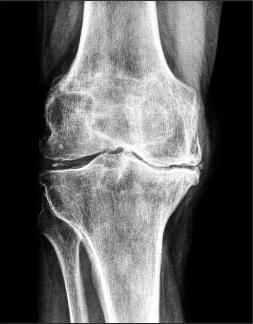
The reasons for the development of osteoarthritis be increased physical activity, low physical activity, metabolic and endocrine disorders. Leading clinical symptoms of disease — pain that increases when walking, functional insufficiency of the knee joint and its deformation. As the progression of osteoarthritis develops ankylosis (complete or partial immobilization of the joints). When setting the diagnosis, the podiatrist focuses on the results of instrumental studies — arthroscopy, radiography, CT, MRI. In the treatment of osteoarthritis of 1 and 2 degrees of severity are used pharmacological agents, physical therapy, offers physiotherapy and massage treatments. With the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy or the detection of pathologies at the final stage, the patient is prepared for total knee replacement.
Characteristic features of the disease
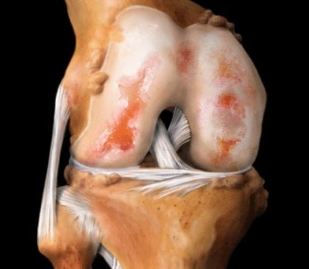
Osteoarthritis of the knee (gonarthrosis) is one of the most frequently diagnosed pathologies affecting the joint. Under the influence of external or internal negative factors in cartilage there is a nutrient deficiency. As a result of disrupted blood supply, slows down the regeneration of connective tissue structures. There is a premature aging hyaline cartilage. He is thin, cracks, becomes rough and loses its strength, firmness and elasticity. Cartilage can no longer perform its main function — the reduction of friction in the joints of bones. Subchondral bone exposed, compacted, they happen osteosclerotic changes. To stabilize the knee joint during walking are growing, flattened the edges of plates of bone with formation of osteophytes (bone spurs).
Osteophytes in the knee joint.
Primary osteoarthritis initially affects the healthy hyaline cartilage due to a congenital reduction in their functional endurance. Secondary pathology occurs when the existing defects of the cartilage tissues. They can be triggered by previous injuries of the knee, inflammation, necrosis, changes in hormonal levels, impaired metabolism.
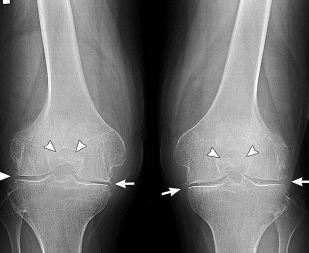
| Clinical-radiological stages of arthrosis of the knee joint | Specific features |
| First | The mobility of the knee joint is slightly reduced, the contours of the joint space become indistinct, slightly converging. At the edges of the bone plates is observed the formation of small amounts of osteophytes |
| Second | When bending or straightening the knee you hear a crunch, clicks, crackle. Muscles moderate atrophy, markedly narrowing the joint space, is formed a significant amount of osteophytes in bone tissue detected by the subchondral osteosclerosis |
| Third | The knee joint is deformed, sharply restricted his mobility. There is a complete or partial fusion of the joint space, a large number of bone spurs, subchondral cysts, pathological masses, freely moving in the cavity of the articulation |
Causes and predisposing factors
The impetus for the development of destructive-degenerative process in hyaline cartilage is usually of several negative factors. The reason for the development of osteoarthritis of the knee in childhood and adolescence are disorders of the formation of the ligament-tendon apparatus, dysplasia. This, in turn, due to hereditary predisposition. Cause the destruction of cartilage can various injuries — fractures, bruises, sprains, partial or complete tears of ligaments, muscles, tendons, meniscus. Excessive stress on the joint provoke the development of disease. Post-traumatic arthritis develops after a few (3 to 5) years after damage to connective or bone structures. Pathology may occur after surgery. And the reason is not the incompetence of doctors, and significant cartilage damage and delayed regeneration. To the disease also predispose to the following factors:

- overweight, in which almost all structures of the musculoskeletal system, and especially the knees are subjected to excessive loads;
- excessive physical activity often leads to microtraining cartilage and the further progression of the destructive processes;
- a sedentary lifestyle, which worsens the blood supply to the legs and a deficit of nutrients in hyaline cartilage;
- systemic inflammatory and degenerative disease — rheumatoid, psoriatic arthritis, gout, osteoporosis, lupus erythematosus.
The clinical picture
In most cases, arthrosis of the knee joint manifests aching, dull pain after regular exercise. The reason for its occurrence becomes irritant effect of osteophytes on the adjacent soft tissues, venous stasis, intra-articular hypertension, muscle spasm. For osteoarthritis typical "start-up" pain, caused by swelling of the joints, or reactive synovitis. When the person long time is in a sitting position, then stands, then take the first steps if there is some soreness. Arise so-called "blockade" pain of a periodic nature. Knee joints while walking is "locked" due to pinched part of the damaged cartilage between the two surfaces of articulation. Also for osteoarthritis, characterized by the following symptoms:
- crepitus, or crunching when you bend or extend your knee that occurs when the displacement of bony structures relative to each other against the background Antoniushof cartilage;
- stiffness, the severity of which increases as the seam of the joint space;
- spasms of the muscles located in the region of the knee, usually appears to reduce the pain;
- deformation of the joints, triggered by destructive changes of the subchondral bone.
With osteoarthritis a person is difficult to climb stairs and go for long walks because of the constant pain of the knee. For pathology is often complicated by synovitis — inflammation of synovial membranes. Clinically they are manifested by the formation of a rounded elastic seal, redness, severe swelling, rise of body temperature to 37.1—38 °C. in the absence of medical intervention arthrosis complicated by spontaneous hemarthrosis (bleeding in the cavity of the knee joint), complete or partial loss of mobility, osteonecrosis of the femoral condyle, the outer subluxation of the patella.
Diagnosis
The clinical picture of arthrosis, especially complicated by synovitis, quite similar to the symptoms of many inflammatory pathologies of the locomotor apparatus. Therefore, differential diagnostics is carried out to exclude arthritis, tendinitis, of tendovaginitis. With the help of research tools define the state of knee articulation and the degree of its functional activity. In the diagnosis of osteoarthritis the most informative radiography. The resulting images clearly visible formed osteophytes, narrowed joint space, deformity of bone structures (cysts, subchondral osteosclerosis). Symmetric narrowing of the joint space of knee joints affected by osteoarthritis. Likely to be surgery have both limbs. A more detailed assessment of changes in the hyaline cartilage allows ultrasound, MRI, CT. Research is also being conducted to identify inflammatory or degenerative lesions of the soft tissues, muscles, ligaments and tendons. If necessary, performed an arthroscopy — a minimally invasive surgical manipulation. In the process of conducting diagnostic procedures are surveyed by the inner surface of the joint, done the fence of biomaterials — the synovial membranes, synovial fluid, and cartilage. When synovitis by means of puncture of the pathological exudate is extracted how to improve the health of the patient, and to study its composition.
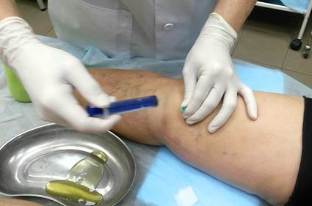
Treatment
Osteoarthritis of the knee 1 severity quite well to therapy with physical therapy and long-term administration of chondroprotectors. Usually requires the use of painkillers, as symptoms are not expressed or absent. For osteoarthritis of the knee 2nd degree is also conducted conservative treatment. But if the disease progresses diagnosed or destruction of significant quantities of cartilage, that the surgery, usually hip replacement. In some cases, patients are shown a fusion — synthetic analogue of ankylosis, or complete immobilization of the knee.
Non-drug therapy
Patients with osteoarthritis 2 or 3 degrees from the first days of treatment is recommended to wear a rigid or semi-rigid orthoses, which significantly restricts the mobility of the knee joint. With minor cartilage damage sufficient use of soft elastic bandages — knee pads. They fix the joint, prevent further destruction of tissue. Patients should reduce physical activity, do not raise heavy weights, to avoid a long walk. Assigned to physiotherapy (5-10 sessions) to improve blood circulation in the knee and stimulate the regeneration of connective tissue structures:
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- high-frequency electrotherapy;
- electrophoresis with anesthetics and chondroprotectors;
- an application of a wax and (or) paraffin.
Strengthen the musculo-ligamentous apparatus and to improve motor function of the knee will help only regular physical therapy sessions. Et doctor selects exercises individually for each patient taking into account the degree of osteoarthritis and physical fitness. The first training was under his control. If the arthritis is strictly prohibited any heavy traffic. They will improve blood circulation, but also provoke even greater microtrauma cartilage. The movement should be smooth, measured, with a small amplitude. In the early stages of gonarthrosis resulting destructive changes of the cartilage can be removed using only physical therapy. Has worked well hirudotherapy, or the treatment of medical leeches. In absence of evidence to the joint put 3-4 leeches, usually in the region of the patella. Segmented worms bite the skin and inject the blood into the saliva with a huge number of biologically active substances.
Pharmacological agents
For elimination of severe pain in the knee are drug blockade with corticosteroids. Hormonal agents are typically combined with anesthetics. Intra-articular injections for osteoarthritis are only performed when absolutely necessary because glucocorticoids characterized by marked side effects. Most commonly in the treatment of arthritis are used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in various dosage forms:
- solutions for parenteral administration;
- tablets;
- ointments and gels.
In the therapeutic scheme must include chondroprotectors in the form of injections or tablets. These funds stimulate the regeneration of worn cartilage, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and anti-edematous action. Any knee pain should be a signal for immediate treatment by the podiatrist. Timely treatment of osteoarthritis will help to avoid severe complications, in some cases, prevent disability of the patient.

















































